Introduction:
Forced labor is a serious violation of human rights, and its legal framework intersects significantly with human rights laws. Forced labor refers to situations where individuals are coerced, threatened, or deceived into working against their will under the threat of punishment or other forms of exploitation. These practices are often associated with severe human rights abuses, including physical and mental abuse, exploitation, and denial of basic freedoms. Forced labor laws are designed to combat these practices, but their relationship to broader human rights laws reflects a shared commitment to dignity, freedom, and justice for all individuals.
1. International Legal Frameworks
The most important international instruments that address forced labor are also grounded in human rights principles. The Universal Declaration of Human Rights, adopted by the United Nations (UN) in 1948, outlines the fundamental rights and freedoms that every person is entitled to, including the right to be free from slavery and forced labor. Article 4 of the UDHR specifically states, "No one shall be held in slavery or servitude; slavery and the slave trade shall be prohibited in all their forms."
Forced Labor Law are directly related to this fundamental principle of human dignity and freedom. These conventions are legally binding international agreements that aim to eliminate forced labor and provide measures for victim protection and justice. These conventions are part of the broader human rights movement and work in tandem with other human rights laws, such as the UDHR and the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, to establish a comprehensive legal framework for the protection of individual freedom.
2. Human Trafficking and Forced Labor
Human Trafficking Forced Labor is often a key factor in the perpetuation of forced labor. Many victims of forced labor are trafficked for the purpose of exploitation, typically through deceptive or coercive means. In this context, human trafficking laws and forced labor laws are closely interconnected with human rights principles. Human trafficking, like forced labor, infringes on basic human rights by stripping individuals of their freedom, security, and dignity.
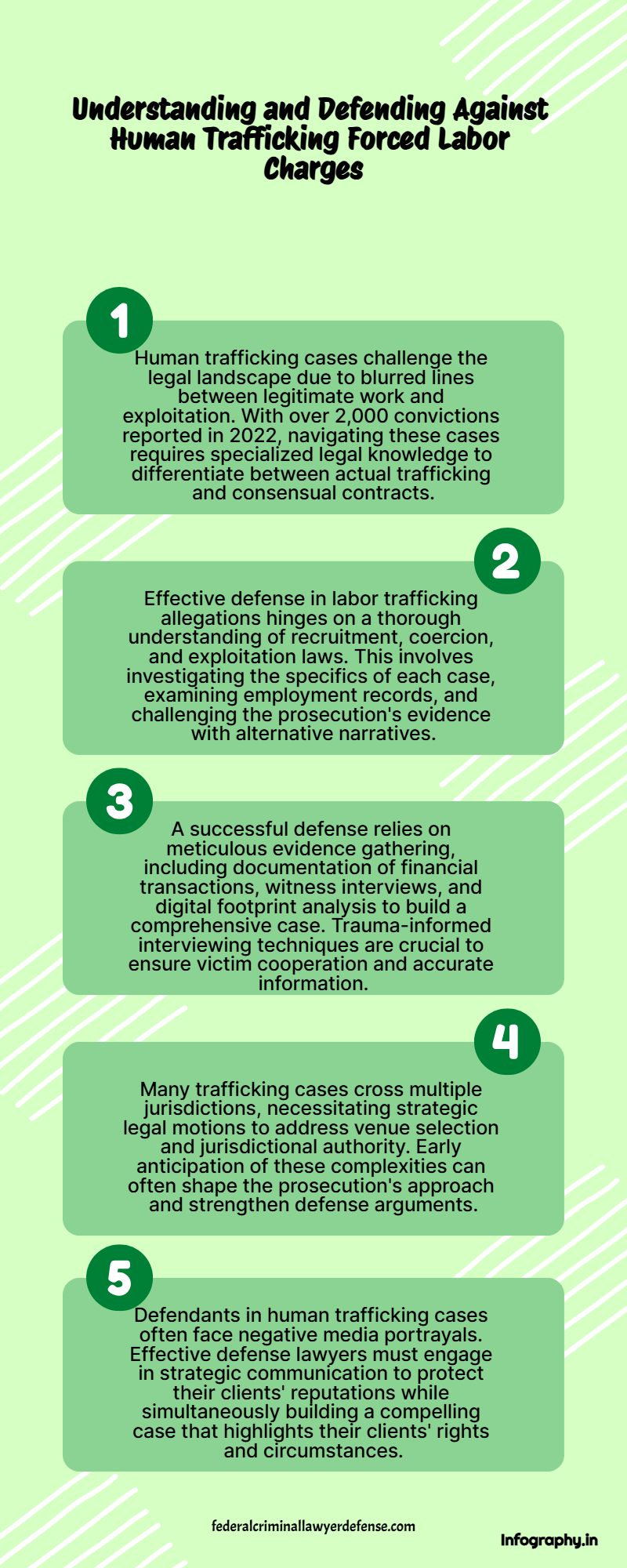
International treaties such as the UN Protocol to Prevent, Suppress, and Punish Trafficking in Persons, Especially Women and Children (2000) aim to combat human trafficking and provide protections for victims. These laws underscore the global commitment to preventing human trafficking, as it is inherently tied to the violation of human rights. The relationship between forced labor and human trafficking demonstrates how labor laws can serve as a critical tool in the protection of human rights, particularly for the most vulnerable individuals.
3. National Legal Systems and Forced Labor
In addition to international conventions, many countries have their own laws that prohibit forced labor and provide mechanisms for the protection of workers’ rights. These national laws are often influenced by international human rights treaties and principles. For example, in the United States, the Trafficking Victims Protection Act criminalizes human trafficking and provides legal frameworks for prosecuting forced labor cases.
National legal systems that incorporate forced labor laws often create a legal duty for employers and businesses to ensure that their operations are free from forced labor, which is a violation of human rights. Laws such as the UK’s Modern Slavery Act of 2015 also require businesses to take steps to address and report any involvement in forced labor within their supply chains. These laws contribute to the global movement to uphold human rights by making forced labor both a criminal act and a violation of the right to work in freedom and dignity.
4. Victim Protection and Rehabilitation
The protection of individuals who have been subjected to forced labor is a key component of both forced labor laws and human rights laws. Human rights frameworks emphasize the right to seek remedy and justice, ensuring that victims of forced labor can access support services, including shelter, medical care, legal aid, and psychological counseling. Forced labor laws, therefore, not only focus on the prevention of such exploitation but also on the rehabilitation and reintegration of victims into society.
National legal systems that address forced labor often establish victim compensation programs, and some international conventions call for the creation of systems to provide immediate assistance to survivors of forced labor and human trafficking. The relationship between forced labor and human rights laws ensures that victims receive both legal protections and the support needed for their recovery, reflecting the broader commitment to human dignity Forgery Lawyer.
5. Corporate Responsibility and Forced Labor
The role of businesses in the prevention of forced labor has gained significant attention in recent years. Forced labor is often hidden within global supply chains, and international human rights laws have increasingly emphasized the role of companies in ensuring that their operations do not involve exploitative labor practices. The UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights provide a framework for corporate responsibility to respect human rights, including the right to be free from forced labor.
These principles hold businesses accountable for the human rights abuses within their supply chains, encouraging transparency and due diligence in monitoring labor practices. Companies are encouraged to take proactive steps to prevent forced labor and report their efforts, ensuring compliance with both human rights standards and national labor laws.
Conclusion
Forced labor laws are deeply intertwined with human rights laws, reflecting the global commitment to protecting individual freedom, dignity, and security. These laws work together to address the exploitation of individuals through forced labor, ensuring that victims are protected and that perpetrators are held accountable. International conventions, national legal frameworks, and corporate responsibility initiatives all contribute to the fight against forced labor, emphasizing that the protection of human rights is central to eliminating this form of modern slavery. By upholding both forced labor laws and human rights principles, societies can work toward the eradication of this grave human rights violation and safeguard the freedom of all individuals.
Comments